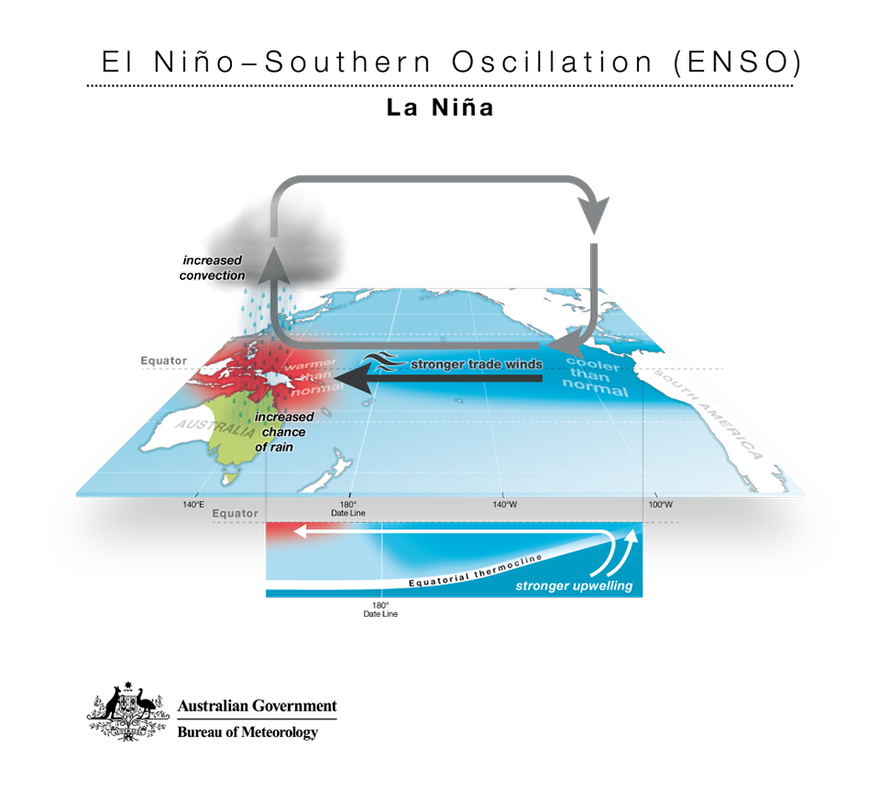
La Nina is characterized by cooler-than-average of sea surface temperature at the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
?????????????? ?? ?????
La Nina is a natural climate phenomenon which refers to the periodic cooling of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, and it is a natural part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle. La Niña events typically develop every two to seven years and can persist for several months to over a year. El Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, La Niña, its cooler counterpart, brings about its own distinctive set of weather patterns across the globe. La Nina occurs when the trade wind at the Pacific Ocean (blow from east Pacific to west Pacific) becomes stronger. This will push warmer surface water to the western side of the Pacific Ocean which is Asian region. This leads to an upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich waters along the coasts of South America. As a result, cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures prevail in the central and eastern Pacific while western Pacific experience warmer surface water. The effects of La Niña are far-reaching and can influence weather patterns across the globe. It can exacerbate existing weather extremes, leading to droughts in some regions and flooding in others. La Nina will cause the Southeast Asian region to experience more rainfall, cooler temperature and increase in flooding cases. Conversely, parts of Africa and South America region will face warmer and dryer conditions. La Niña also tends to enhance hurricane activity in the Atlantic Basin while suppressing it in the Pacific Basin. This can lead to an increase in the number of hurricanes and tropical storms forming in the Atlantic, potentially posing risks to coastal communities. Meteorologists closely monitor sea surface temperatures, atmospheric pressure patterns, and other indicators to predict the onset and intensity of La Niña events. Advanced climate models and data from satellites and ocean buoys help forecasters anticipate its potential impacts on weather patterns months in advance, allowing governments and communities to prepare and mitigate risks. In conclusion, La Niña is a natural climatic phenomenon with far-reaching effects on weather patterns worldwide. Understanding its causes and impacts is crucial for policymakers, meteorologists, and communities to better prepare for and adapt to the associated weather extremes. As our understanding of climate variability continues to evolve, so does our ability to anticipate and respond to events like La Niña, ultimately contributing to greater resilience in the face of a changing climate. #lanina #Climate#event #oceanhydro
